11.1 Key assumptions used to calculate value in use
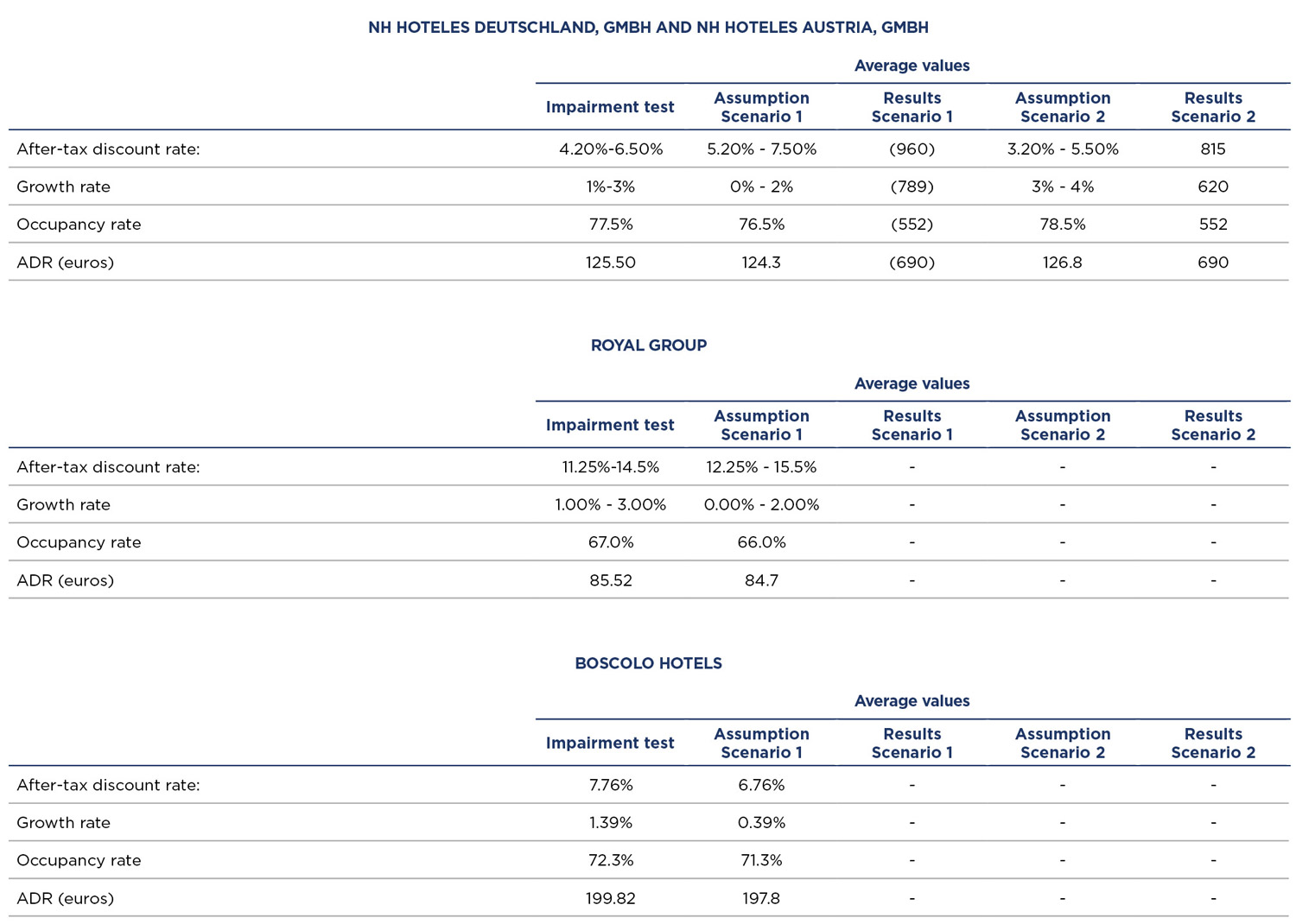
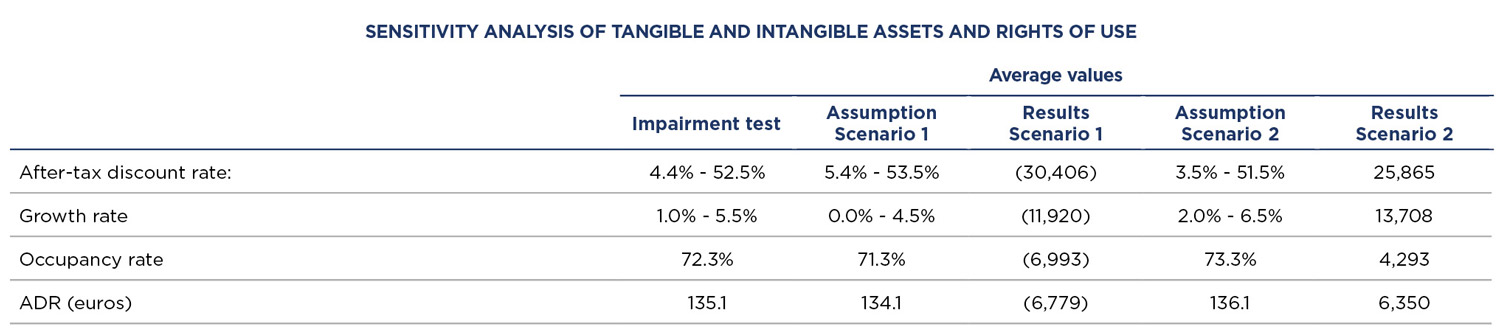
The evolution of the key assumptions in the analysed hotels has taking the business knowledge of Group Management into account as well as the expected recovery of the sector after the COVID-19 pandemic. In this regard, the assumed projections are based on the use of the Management’s budget for 2022, which assumes a dramatic recovery in revenues compared to 2021, but still lower than those in 2019 due to the negative effect that the COVID-19 pandemic has had on tourism over the past two years. Recovery to pre-COVID-19 levels is calculated in the comparable hotels over the next few years, once mobility restrictions decrease and, therefore, consumer confidence is recovered. The Group’s strong positioning in the countries where it operates, the good locations of the portfolio and the high recognition of its brands are key factors in the assumed recovery period. This recovery scenario calculates reaching pre-pandemic figures in the comparable hotels, which are those for 2019, between 2023 and 2024.
There are a number of factors that are considered by the Group’s Management to make the projections, which are:
-
- Estimate of external sources specialising in the hotel sector, along with investment banks with reference to the recovery of the hotel sector.
- Estimate of GDP (Gross Domestic Product) growth issued by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) in its report published in October of each year for the next five years.
- Knowledge of the business/asset/local situation of the local Management of each Business Unit to which each CGU belongs.
- Historical results obtained by the CGUs.
- Investments in repositioning the CGUs.
These factors are reflected in the cash flows through the following working hypotheses used to obtain the projections:
-
- Income from accommodation is projected as the product of percentage occupation, and average rate per room (“ADR” Average Daily Rate: is the ratio of the total income from rooms in a specific period divided by the rooms sold in that specific period) and the total rooms available per year.
- The other revenues are projected based on the average of the relationship between the revenue from accommodation and those revenues.
- Personnel expenses are calculated on the basis of the average cost for personnel plus the relevant increase in each country referenced to the collective employment agreement for each year.
- Direct expenses are directly associated with each of the revenues and are projected on the basis of an average ratio, while undistributed expenses are projected based on the average ratio between these and direct expenses.
- For its part, tax is calculated from the tax rates applicable in each country.
The discount rates were calculated by a third party using the Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) methodology: Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC), as follows:
WACC=Ke*E/(E+D) + Kd*(1-T)*D/(E+D)
Where:
Ke: Cost of Equity
Kd: Cost of Financial Debt
E: Own Funds
D: Financial Debt
T: Tax Rate
The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) is used to estimate the cost of equity (ke).
The main variables used by a third party to calculate the discount rate are as follows:
-
- Risk-free rate: the WACC calculation is based on an increased risk-free rate. The risk-free rate is standardised to show the average sustainable performance of the long-term bonds issued by governments and considered to be “safe” (usually those classified as AAA by the main ratings agencies).
- For European countries, a rate of 0% was taken into account as the performance of German government bonds at 20 years, on the valuation date, showed negative performance from December 2021 and a 1.5% standardisation was extended.
- For Latin American countries, American sovereign debt was taken into account, which oscillates between 1.8% (performance at the Valuation Date) and 2.5% (standardised value). In these countries, the differential of inflation to the USA is also applied.
- For the United Kingdom, the performance of British government bonds at 20 years was taken into account, which oscillates between 1.2% (performance at the Valuation Date) and 2.5% (standardised value).
- Market risks premium: defined at 5.5% for rates in EUR and USD and 5.0% for GBP, based on a wide range of financial information, multiple methodologies and economic and financial market conditions at December 2021.
- Beta or systematic risk: Using a sample of listed companies whose businesses are comparable, the sector’s risk differential is estimated in relation to the average risk on the global market. To calculate the WACC for hotels being leased, a comparative of a sample of traditional hotel companies is taken into account. Furthermore, to this group, and to calculate the WACC for owned hotels, a sample of property investment funds (REITs) is also included in order to show the real estate contribution to the business. Bloomberg’s historic betas were taken as a reference (monthly data at 5 years). Given that these betas are leveraged, they have been de-leveraged taking into account the average historical debt/capital structure for each company over 5 years.
- The capital structure applied was estimated on the basis of the capital structure of the comparable companies, taking the proportion of debt with interest, preferential capital and ordinary capital of these companies that are listed on the stock exchange into consideration. The average capital structure applied is 59.5% Own Funds and 40.5% Debt for the group of comparables for owned hotels, and 58.1% Own Funds and 41.9% Debt for the group of comparables for leased hotels.
- In addition, the local rate for corporation tax on the valuation date in each country was considered.
- To calculate the Cost of the debt, a 2.9% debt differential is applied, based on the spot rate of German bonds at 20 years and applying the credit rating differential for the comparable companies of reference.
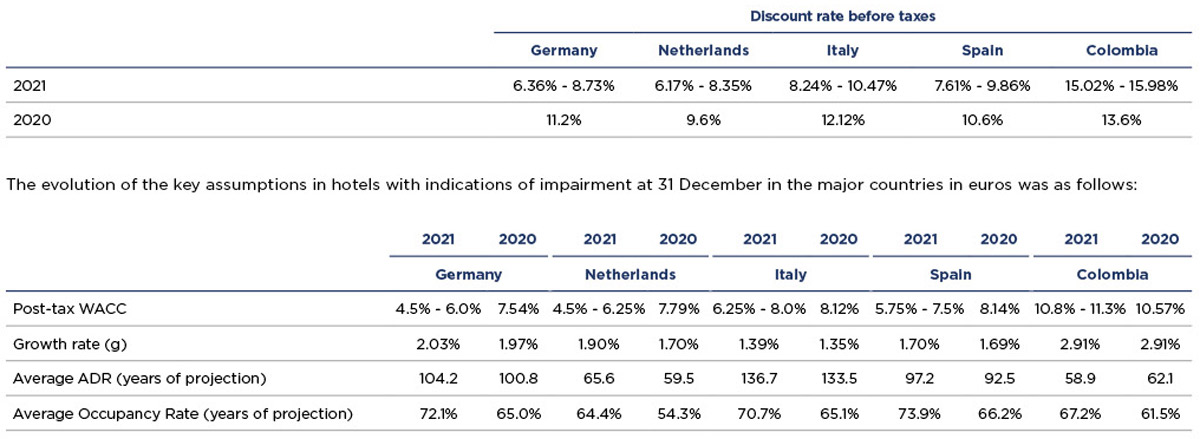
Below are the pre-tax discount rates of the major countries: